Difference between revisions of "KinC"
(→Basic information/ Evolution) |
|||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
=== Basic information/ Evolution === | === Basic information/ Evolution === | ||
| − | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' phosphorylation of [[Spo0F]] as part of the [[phosphorelay]], but also direct phosphorylation of [[Spo0A]] {{PubMed|19114652}} | + | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' autophosphorylation, phosphorylation of [[Spo0F]] as part of the [[phosphorelay]], but also direct phosphorylation of [[Spo0A]] {{PubMed|19114652}} |
* '''Protein family:''' | * '''Protein family:''' | ||
Revision as of 19:51, 30 November 2009
- Description: two-component sensor kinase, phosphorylates Spo0F and Spo0A, part of the phosphorelay
| Gene name | kinC |
| Synonyms | ssb |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component sensor kinase |
| Function | initiation of sporulation |
| MW, pI | 48 kDa, 6.225 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1284 bp, 428 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | abh, ykqA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 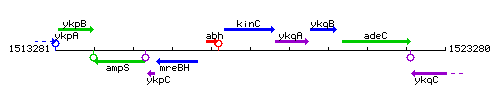
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU14490
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: autophosphorylation, phosphorylation of Spo0F as part of the phosphorelay, but also direct phosphorylation of Spo0A PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: two transmembrane segments, C-terminal histidine phosphotransferase domain
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: activity is triggered by potassium leakage PubMed
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot), Membrane (Heterogeneous) PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39764
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: kinC (according to DBTBS)
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Daniel López, Michael A Fischbach, Frances Chu, Richard Losick, Roberto Kolter
Structurally diverse natural products that cause potassium leakage trigger multicellularity in Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2009, 106(1);280-5
[PubMed:19114652]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jean-Christophe Meile, Ling Juan Wu, S Dusko Ehrlich, Jeff Errington, Philippe Noirot
Systematic localisation of proteins fused to the green fluorescent protein in Bacillus subtilis: identification of new proteins at the DNA replication factory.
Proteomics: 2006, 6(7);2135-46
[PubMed:16479537]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Masaya Fujita, Richard Losick
Evidence that entry into sporulation in Bacillus subtilis is governed by a gradual increase in the level and activity of the master regulator Spo0A.
Genes Dev: 2005, 19(18);2236-44
[PubMed:16166384]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Jiang, W Shao, M Perego, J A Hoch
Multiple histidine kinases regulate entry into stationary phase and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2000, 38(3);535-42
[PubMed:11069677]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C Fabret, V A Feher, J A Hoch
Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: how one organism sees its world.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(7);1975-83
[PubMed:10094672]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Kobayashi, K Shoji, T Shimizu, K Nakano, T Sato, Y Kobayashi
Analysis of a suppressor mutation ssb (kinC) of sur0B20 (spo0A) mutation in Bacillus subtilis reveals that kinC encodes a histidine protein kinase.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(1);176-82
[PubMed:8002615]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J R LeDeaux, A D Grossman
Isolation and characterization of kinC, a gene that encodes a sensor kinase homologous to the sporulation sensor kinases KinA and KinB in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(1);166-75
[PubMed:8002614]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)