Difference between revisions of "CitB"
m (Reverted edits by 134.76.70.252 (talk) to last revision by Jstuelk) |
|||
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
** repression by glucose + arginine ([[CcpC]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16395550 PubMed] | ** repression by glucose + arginine ([[CcpC]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16395550 PubMed] | ||
** less expressed under conditions of extreme iron limitation ([[FsrA]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18697947 PubMed] | ** less expressed under conditions of extreme iron limitation ([[FsrA]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18697947 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** part of the iron sparing response ([[FsrA]]) {{PubMed|22389480}} | ||
* '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | ||
| Line 127: | Line 128: | ||
** [[CcpC]]: transcription repression (molecular inducer: citrate) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10656796 PubMed1] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12100558 PubMed2] | ** [[CcpC]]: transcription repression (molecular inducer: citrate) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10656796 PubMed1] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12100558 PubMed2] | ||
** [[CcpA]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12100558 PubMed] | ** [[CcpA]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12100558 PubMed] | ||
| − | ** [[FsrA]]: translational repression | + | ** [[FsrA]]: translational repression {{PubMed|18697947}} |
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
| Line 158: | Line 159: | ||
<pubmed> 12732309 2696478 18261896 18086213 </pubmed> | <pubmed> 12732309 2696478 18261896 18086213 </pubmed> | ||
==Original publications== | ==Original publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>18697947, 20097860,2118511,12591885,10656796,12591885,12850135 2413006 10656796 10468622 6143742 12591885 16395550 16923907 9642180 9393699 12591885 2105305,20933603 21099137 21446632 21821766</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>18697947, 20097860,2118511,12591885,10656796,12591885,12850135 2413006 10656796 10468622 6143742 12591885 16395550 16923907 9642180 9393699 12591885 2105305,20933603 21099137 21446632 21821766 22389480</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 18:07, 14 March 2012
- Description: trigger enzyme: aconitase and RNA binding protein
| Gene name | citB |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | trigger enzyme: aconitate hydratase (aconitase) |
| Function | TCA cycle |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: CitB | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 99 kDa, 4.903 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2727 bp, 909 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | sspO, yneN |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 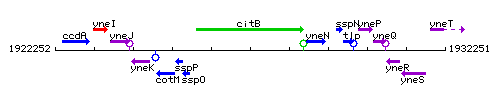
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
carbon core metabolism, trigger enzyme, RNA binding regulators
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CcpC regulon, CodY regulon, FsrA regulon
The CitB regulon: feuA-feuB-feuC-ybbA
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU18000
Phenotypes of a mutant
glutamate auxotrophy and a defect in sporulation PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
- A mutation was found in this gene after evolution under relaxed selection for sporulation PubMed
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Citrate = isocitrate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Binding to iron responsive elements (IRE RNA) in the absence of the FeS cluster PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s): FeS cluster
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure: 1L5J (E. coli)
- UniProt: P09339
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 4.2.1.3
Additional information
- B. subtilis aconitase is both an enzyme and an RNA binding protein (moonlighting protein) PubMed
- extensive information on the structure and enzymatic properties of CitB can be found at Proteopedia
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- repressed during growth in the presence of branched chain amino acids (CodY) PubMed
- repressed in the presence of glucose and glutamate (CcpC) PubMed
- expressed upon transition into the stationary phase (AbrB) PubMed, indirect negative regulation by AbrB PubMed
- repressed by glucose (3.7-fold) (CcpA) PubMed
- repression by glucose + arginine (CcpC) PubMed
- less expressed under conditions of extreme iron limitation (FsrA) PubMed
- part of the iron sparing response (FsrA) PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP683 (erm), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody: available in Linc Sonenshein lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Karl Volz
The functional duality of iron regulatory protein 1.
Curr Opin Struct Biol: 2008, 18(1);106-11
[PubMed:18261896]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Fabian M Commichau, Jörg Stülke
Trigger enzymes: bifunctional proteins active in metabolism and in controlling gene expression.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 67(4);692-702
[PubMed:18086213]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Patricia J Kiley, Helmut Beinert
The role of Fe-S proteins in sensing and regulation in bacteria.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2003, 6(2);181-5
[PubMed:12732309]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
R L Switzer
Non-redox roles for iron-sulfur clusters in enzymes.
Biofactors: 1989, 2(2);77-86
[PubMed:2696478]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)
Original publications