Difference between revisions of "FtsZ"
(→Reviews) |
|||
| Line 159: | Line 159: | ||
==Reviews== | ==Reviews== | ||
| − | <pubmed>22047950</pubmed> | + | '''Additional reviews:''' {{PubMed|21119015}} |
| + | <pubmed>22047950 22575476 </pubmed> | ||
<pubmed> 19680248 19884039 17506674 15037301 21047262 21981908</pubmed> | <pubmed> 19680248 19884039 17506674 15037301 21047262 21981908</pubmed> | ||
| − | |||
==FtsZ as antibacterial drug target== | ==FtsZ as antibacterial drug target== | ||
Revision as of 12:06, 14 May 2012
- Description: cell-division initiation protein (septum formation)
| Gene name | ftsZ |
| Synonyms | ts-1 |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | cell-division initiation protein (septum formation) |
| Function | formation of Z-ring |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: FtsZ | |
| MW, pI | 40 kDa, 4.814 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1146 bp, 382 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ftsA, bpr |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 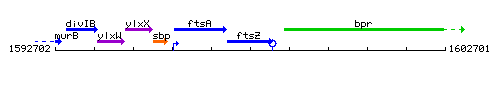
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed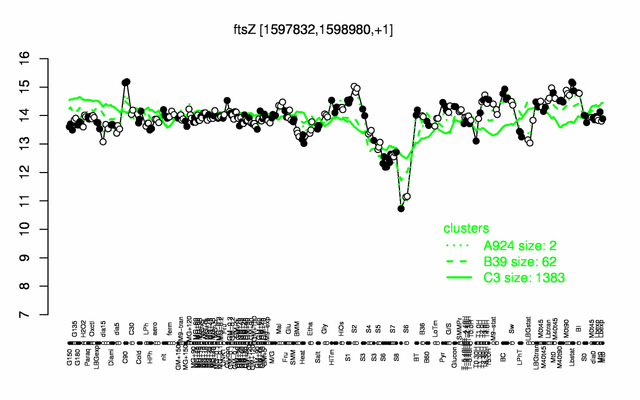
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell division, essential genes, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15290
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ftsZ family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- UniProt: P17865
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody: available in the Jeff Errington lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
- Imrich Barak, Slovak Academy of Science, Bratislava, Slovakia homepage
- Leendert Hamoen, CBCB, Newcastle University, UK
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Additional reviews: PubMed
An-Chun Chien, Norbert S Hill, Petra Anne Levin
Cell size control in bacteria.
Curr Biol: 2012, 22(9);R340-9
[PubMed:22575476]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Kaimer, Peter L Graumann
Players between the worlds: multifunctional DNA translocases.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2011, 14(6);719-25
[PubMed:22047950]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Clare L Kirkpatrick, Patrick H Viollier
New(s) to the (Z-)ring.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2011, 14(6);691-7
[PubMed:21981908]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Matthew T Cabeen, Christine Jacobs-Wagner
The bacterial cytoskeleton.
Annu Rev Genet: 2010, 44;365-92
[PubMed:21047262]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Marc Bramkamp, Suey van Baarle
Division site selection in rod-shaped bacteria.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2009, 12(6);683-8
[PubMed:19884039]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
David W Adams, Jeff Errington
Bacterial cell division: assembly, maintenance and disassembly of the Z ring.
Nat Rev Microbiol: 2009, 7(9);642-53
[PubMed:19680248]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Peter L Graumann
Cytoskeletal elements in bacteria.
Annu Rev Microbiol: 2007, 61;589-618
[PubMed:17506674]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Linda A Amos, Fusinita van den Ent, Jan Löwe
Structural/functional homology between the bacterial and eukaryotic cytoskeletons.
Curr Opin Cell Biol: 2004, 16(1);24-31
[PubMed:15037301]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
FtsZ as antibacterial drug target
David W Adams, Ling Juan Wu, Lloyd G Czaplewski, Jeff Errington
Multiple effects of benzamide antibiotics on FtsZ function.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 80(1);68-84
[PubMed:21276094]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Simranjeet Kaur, Niraj H Modi, Dulal Panda, Nilanjan Roy
Probing the binding site of curcumin in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis FtsZ--a structural insight to unveil antibacterial activity of curcumin.
Eur J Med Chem: 2010, 45(9);4209-14
[PubMed:20615583]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kumiko W Shimotohno, Fujio Kawamura, Yousuke Natori, Hideaki Nanamiya, Junji Magae, Hiromitsu Ogata, Toyoshige Endo, Takeshi Suzuki, Hiroshi Yamaki
Inhibition of septation in Bacillus subtilis by a peptide antibiotic, edeine B(1).
Biol Pharm Bull: 2010, 33(4);568-71
[PubMed:20410587]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
José M Andreu, Claudia Schaffner-Barbero, Sonia Huecas, Dulce Alonso, María L Lopez-Rodriguez, Laura B Ruiz-Avila, Rafael Núñez-Ramírez, Oscar Llorca, Antonio J Martín-Galiano
The antibacterial cell division inhibitor PC190723 is an FtsZ polymer-stabilizing agent that induces filament assembly and condensation.
J Biol Chem: 2010, 285(19);14239-46
[PubMed:20212044]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Tushar K Beuria, Parminder Singh, Avadhesha Surolia, Dulal Panda
Promoting assembly and bundling of FtsZ as a strategy to inhibit bacterial cell division: a new approach for developing novel antibacterial drugs.
Biochem J: 2009, 423(1);61-9
[PubMed:19583568]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Neil R Stokes, Jörg Sievers, Stephanie Barker, James M Bennett, David R Brown, Ian Collins, Veronica M Errington, David Foulger, Michelle Hall, Rowena Halsey, Hazel Johnson, Valerie Rose, Helena B Thomaides, David J Haydon, Lloyd G Czaplewski, Jeff Errington
Novel inhibitors of bacterial cytokinesis identified by a cell-based antibiotic screening assay.
J Biol Chem: 2005, 280(48);39709-15
[PubMed:16174771]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Other original Publications
Additional publications: PubMed