Difference between revisions of "MreB"
(→Other original publications) |
(→Reviews) |
||
| Line 154: | Line 154: | ||
==Reviews== | ==Reviews== | ||
'''Additional reviews:''' {{PubMed|21371139}} | '''Additional reviews:''' {{PubMed|21371139}} | ||
| − | <pubmed>17506674 17158703 15037301 21725336 20825347 21047262 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>17506674 17158703 15037301 21725336 20825347 21047262 22166997</pubmed> |
==Localization== | ==Localization== | ||
Revision as of 09:19, 30 December 2011
- Description: cell shape-determining protein, forms filaments, the polymers control/restrict the mobility of the cell wall elongation enzyme complex
| Gene name | mreB |
| Synonyms | divIVB |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | cell shape-determining protein |
| Function | cell shape determination |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: MreB | |
| MW, pI | 35 kDa, 4.901 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1011 bp, 337 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | mreC, radC |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 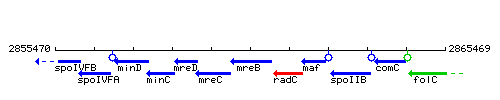
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell shape, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y), essential genes, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU28030
Phenotypes of a mutant
- essential PubMed
- the mutation can be suppressed by inactivation of ponA, ptsI, ccpA PubMed, by overexpression of YvcK PubMed, or by addition of 5 mM magnesium to the growth medium PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ftsA/mreB family (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- during logarithmic growth, MreB forms discrete patches thst move processively along peripheral tracks perpendicular to the cell axis PubMed
- forms transverse bands as cells enter the stationary phase PubMed
- close to the inner surface of the cytoplasmic membrane PubMed
- reports on helical structures formed by MreB PubMed seem to be misinterpretation of data PubMed
Database entries
- UniProt: Q01465
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in the labs of Jeff Errington and Boris Görke
- Antibody: available in the Jeff Errington and Peter Graumann labs
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jeff Errington, Newcastle University, UK homepage
Peter Graumann, Freiburg University, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Additional reviews: PubMed
Sven van Teeffelen, Zemer Gitai
Rotate into shape: MreB and bacterial morphogenesis.
EMBO J: 2011, 30(24);4856-7
[PubMed:22166997]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Andrew Jermy
Bacterial physiology: MreB takes a back seat.
Nat Rev Microbiol: 2011, 9(8);560-1
[PubMed:21725336]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Matthew T Cabeen, Christine Jacobs-Wagner
The bacterial cytoskeleton.
Annu Rev Genet: 2010, 44;365-92
[PubMed:21047262]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kevin D Young
Bacterial shape: two-dimensional questions and possibilities.
Annu Rev Microbiol: 2010, 64;223-40
[PubMed:20825347]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Peter L Graumann
Cytoskeletal elements in bacteria.
Annu Rev Microbiol: 2007, 61;589-618
[PubMed:17506674]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Rut Carballido-López
The bacterial actin-like cytoskeleton.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2006, 70(4);888-909
[PubMed:17158703]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Linda A Amos, Fusinita van den Ent, Jan Löwe
Structural/functional homology between the bacterial and eukaryotic cytoskeletons.
Curr Opin Cell Biol: 2004, 16(1);24-31
[PubMed:15037301]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Localization
Ethan C Garner, Remi Bernard, Wenqin Wang, Xiaowei Zhuang, David Z Rudner, Tim Mitchison
Coupled, circumferential motions of the cell wall synthesis machinery and MreB filaments in B. subtilis.
Science: 2011, 333(6039);222-5
[PubMed:21636745]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Julia Domínguez-Escobar, Arnaud Chastanet, Alvaro H Crevenna, Vincent Fromion, Roland Wedlich-Söldner, Rut Carballido-López
Processive movement of MreB-associated cell wall biosynthetic complexes in bacteria.
Science: 2011, 333(6039);225-8
[PubMed:21636744]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Henrik Strahl, Leendert W Hamoen
Membrane potential is important for bacterial cell division.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2010, 107(27);12281-6
[PubMed:20566861]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hervé Joël Defeu Soufo, Peter L Graumann
Dynamic localization and interaction with other Bacillus subtilis actin-like proteins are important for the function of MreB.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 62(5);1340-56
[PubMed:17064365]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Other original publications
Additional publications: PubMed
Felix Dempwolff, Christian Reimold, Michael Reth, Peter L Graumann
Bacillus subtilis MreB orthologs self-organize into filamentous structures underneath the cell membrane in a heterologous cell system.
PLoS One: 2011, 6(11);e27035
[PubMed:22069484]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yoshikazu Kawai, Jon Marles-Wright, Robert M Cleverley, Robyn Emmins, Shu Ishikawa, Masayoshi Kuwano, Nadja Heinz, Nhat Khai Bui, Christopher N Hoyland, Naotake Ogasawara, Richard J Lewis, Waldemar Vollmer, Richard A Daniel, Jeff Errington
A widespread family of bacterial cell wall assembly proteins.
EMBO J: 2011, 30(24);4931-41
[PubMed:21964069]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Elodie Foulquier, Frédérique Pompeo, Alain Bernadac, Leon Espinosa, Anne Galinier
The YvcK protein is required for morphogenesis via localization of PBP1 under gluconeogenic growth conditions in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 80(2);309-18
[PubMed:21320184]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hervé Joël Defeu Soufo, Peter L Graumann
Bacillus subtilis MreB paralogues have different filament architectures and lead to shape remodelling of a heterologous cell system.
Mol Microbiol: 2010, 78(5);1145-58
[PubMed:21091501]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hervé Joël Defeu Soufo, Christian Reimold, Uwe Linne, Tobias Knust, Johannes Gescher, Peter L Graumann
Bacterial translation elongation factor EF-Tu interacts and colocalizes with actin-like MreB protein.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2010, 107(7);3163-8
[PubMed:20133608]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yoshikazu Kawai, Kei Asai, Jeffery Errington
Partial functional redundancy of MreB isoforms, MreB, Mbl and MreBH, in cell morphogenesis of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 73(4);719-31
[PubMed:19659933]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Daniel Muñoz-Espín, Richard Daniel, Yoshikazu Kawai, Rut Carballido-López, Virginia Castilla-Llorente, Jeff Errington, Wilfried J J Meijer, Margarita Salas
The actin-like MreB cytoskeleton organizes viral DNA replication in bacteria.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2009, 106(32);13347-52
[PubMed:19654094]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kathrin Schirner, Jeff Errington
Influence of heterologous MreB proteins on cell morphology of Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2009, 155(Pt 11);3611-3621
[PubMed:19643765]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yoshikazu Kawai, Richard A Daniel, Jeffery Errington
Regulation of cell wall morphogenesis in Bacillus subtilis by recruitment of PBP1 to the MreB helix.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 71(5);1131-44
[PubMed:19192185]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Joshua A Mayer, Kurt J Amann
Assembly properties of the Bacillus subtilis actin, MreB.
Cell Motil Cytoskeleton: 2009, 66(2);109-18
[PubMed:19117023]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Warawan Eiamphungporn, John D Helmann
The Bacillus subtilis sigma(M) regulon and its contribution to cell envelope stress responses.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 67(4);830-48
[PubMed:18179421]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Rut Carballido-López, Alex Formstone, Ying Li, S Dusko Ehrlich, Philippe Noirot, Jeff Errington
Actin homolog MreBH governs cell morphogenesis by localization of the cell wall hydrolase LytE.
Dev Cell: 2006, 11(3);399-409
[PubMed:16950129]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Alex Formstone, Jeffery Errington
A magnesium-dependent mreB null mutant: implications for the role of mreB in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2005, 55(6);1646-57
[PubMed:15752190]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Richard A Daniel, Jeff Errington
Control of cell morphogenesis in bacteria: two distinct ways to make a rod-shaped cell.
Cell: 2003, 113(6);767-76
[PubMed:12809607]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
F van den Ent, L A Amos, J Löwe
Prokaryotic origin of the actin cytoskeleton.
Nature: 2001, 413(6851);39-44
[PubMed:11544518]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L J Jones, R Carballido-López, J Errington
Control of cell shape in bacteria: helical, actin-like filaments in Bacillus subtilis.
Cell: 2001, 104(6);913-22
[PubMed:11290328]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Abhayawardhane, G C Stewart
Bacillus subtilis possesses a second determinant with extensive sequence similarity to the Escherichia coli mreB morphogene.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(3);765-73
[PubMed:7836311]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Lee, C W Price
The minCD locus of Bacillus subtilis lacks the minE determinant that provides topological specificity to cell division.
Mol Microbiol: 1993, 7(4);601-10
[PubMed:8459776]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
P A Levin, P S Margolis, P Setlow, R Losick, D Sun
Identification of Bacillus subtilis genes for septum placement and shape determination.
J Bacteriol: 1992, 174(21);6717-28
[PubMed:1400224]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)