Difference between revisions of "HypR"
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || control of the nitroreductase gene ''[[hypO]]'' in response to disulfide stress (diamide, NaOCl) | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || control of the nitroreductase gene ''[[hypO]]'' in response to disulfide stress (diamide, NaOCl) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Gene expression levels in [http:// | + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Gene expression levels in [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/ ''Subti''Express]''': [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/expression.php?search=BSU40540 hypR] |
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 14 kDa, 8.415 | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 14 kDa, 8.415 | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[cotF]]'', ''[[ppaC]]'' | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[cotF]]'', ''[[ppaC]]'' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Sequences'''||[http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence-aa?type=GENE&object=BSU40540 Protein] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence?type=GENE&object=BSU40540 DNA] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/seq-selector?chromosome=CHROM-1&object=BSU40540 Advanced_DNA] |
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:yybR_context.gif]] | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:yybR_context.gif]] | ||
Revision as of 14:19, 13 May 2013
- Description: MarR/DUF24 family transcription regulator, positively controls the nitroreductase gene hypO in response to disulfide stress
| Gene name | hypR |
| Synonyms | yybR |
| Essential | no |
| Product | MarR/DUF24 family transcription regulator HypR |
| Function | control of the nitroreductase gene hypO in response to disulfide stress (diamide, NaOCl) |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: hypR | |
| MW, pI | 14 kDa, 8.415 |
| Gene length, protein length | 375 bp, 125 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | cotF, ppaC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA Advanced_DNA |
Genetic context 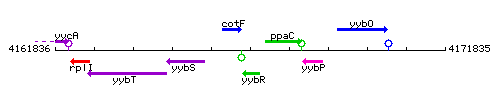
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed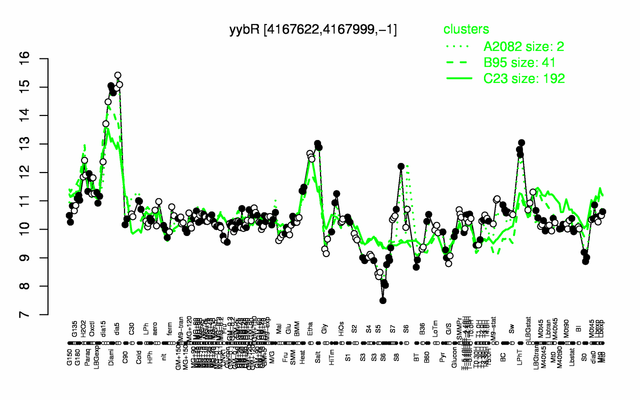
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, resistance against oxidative and electrophile stress
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The HypR regulon:
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU40540
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
- hypR is autoregulated by disulfide stress
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: MarR/DUF24 family
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information: Cys14 redox sensing Cys, has lower pKa of 6.36 PubMed
- Domains:
- 5 alpha helices, 2 beta sheets, MarR-fold with wHTH motif, alpha4 major groove recognition helix, beta2 and 3 form the wing; alpha5 dimer interface PubMed
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cytoplasmic
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P37486
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: hypR PubMed
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation:
- activated by disulfide stress conditions (diamide, NaOCl) in vivo and in vitro (autoregulation) PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
- Haike Antelmann,University of Greifswald, Germany
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Antelmann H, Helmann JD. Thiol-based redox switches and gene regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011,14:1049-63. PubMed
Original articles
Palm GJ, Khanh Chi B, Waack P, Gronau K, Becher D, Albrecht D, Hinrichs W, Read RJ, Antelmann H. Structural insights into the redox-switch mechanism of the MarR/DUF24-type regulator HypR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, Jan 11. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed