Difference between revisions of "DctP"
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Gene expression levels in [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/ ''Subti''Express]''': [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/expression.php?search=BSU04470 dctP] | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Gene expression levels in [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/ ''Subti''Express]''': [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/expression.php?search=BSU04470 dctP] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Interactions involving this protein in [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/interact/ ''Subt''Interact]''': [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/interact/index.php?protein=DctP DctP] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/carbon_flow.html Central C-metabolism]''' | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/carbon_flow.html Central C-metabolism]''' | ||
| Line 68: | Line 70: | ||
=== Basic information/ Evolution === | === Basic information/ Evolution === | ||
| − | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' uptake of succinate, fumurate, malate and oxaloacetate via proton symport {{PubMed|20363944}} | + | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' |
| + | ** uptake of succinate, fumurate, malate and oxaloacetate via proton symport {{PubMed|20363944}} | ||
| + | ** acts as co-sensor for [[DctS]] {{PubMed|24375102}} | ||
* '''Protein family:''' View classification (according to Swiss-Prot) | * '''Protein family:''' View classification (according to Swiss-Prot) | ||
| Line 87: | Line 91: | ||
* '''[[SubtInteract|Interactions]]:''' | * '''[[SubtInteract|Interactions]]:''' | ||
| + | ** [[DctB]]-[[DctS]]-[[DctP]], sensing complex {{PubMed|24375102}} | ||
* '''[[Localization]]:''' | * '''[[Localization]]:''' | ||
| Line 145: | Line 150: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>12850135, 10708364 10627041, 12949159 20363944 22389480 22900538 24013209</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>12850135, 10708364 10627041, 12949159 20363944 22389480 22900538 24013209 24375102</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 16:29, 2 January 2014
- Description: uptake of succinate, fumurate, malate and oxaloacetate via proton symport
| Gene name | dctP |
| Synonyms | ydbH, dctA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | C4-dicarboxylate transport protein |
| Function | uptake of succinate, fumurate, malate and oxaloacetate |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: dctP | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: DctP | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 45 kDa, 8.668 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1263 bp, 421 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | dctR, ydbI |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 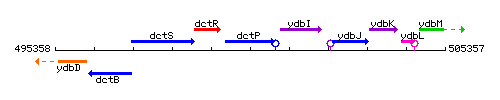
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed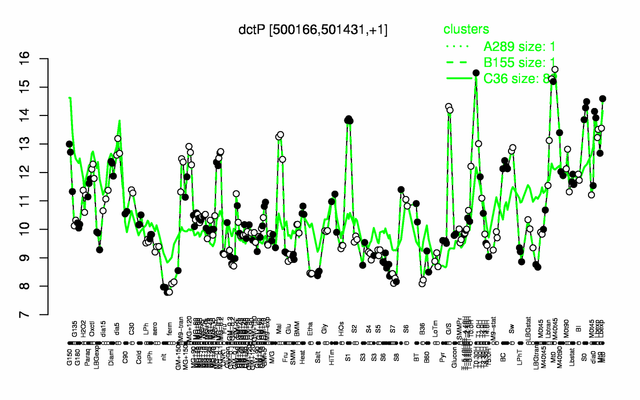
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transporters/ other, utilization of specific carbon sources, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU04470
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: View classification (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure: 4KY0 (the glutamate transporter of Thermococcus kodakarensis, 31% identity, 71% similarity) PubMed
- UniProt: P96603
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Sabrina Graf, Dominik Schmieden, Karolin Tschauner, Sabine Hunke, Gottfried Unden
The sensor kinase DctS forms a tripartite sensor unit with DctB and DctA for sensing C4-dicarboxylates in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2014, 196(5);1084-93
[PubMed:24375102]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Sonja Jensen, Albert Guskov, Stephan Rempel, Inga Hänelt, Dirk Jan Slotboom
Crystal structure of a substrate-free aspartate transporter.
Nat Struct Mol Biol: 2013, 20(10);1224-6
[PubMed:24013209]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Bogumiła C Marciniak, Monika Pabijaniak, Anne de Jong, Robert Dűhring, Gerald Seidel, Wolfgang Hillen, Oscar P Kuipers
High- and low-affinity cre boxes for CcpA binding in Bacillus subtilis revealed by genome-wide analysis.
BMC Genomics: 2012, 13;401
[PubMed:22900538]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Gregory T Smaldone, Olga Revelles, Ahmed Gaballa, Uwe Sauer, Haike Antelmann, John D Helmann
A global investigation of the Bacillus subtilis iron-sparing response identifies major changes in metabolism.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(10);2594-605
[PubMed:22389480]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Maarten Groeneveld, Ruud G J Detert Oude Weme, Ria H Duurkens, Dirk Jan Slotboom
Biochemical characterization of the C4-dicarboxylate transporter DctA from Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(11);2900-7
[PubMed:20363944]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kousei Tanaka, Kazuo Kobayashi, Naotake Ogasawara
The Bacillus subtilis YufLM two-component system regulates the expression of the malate transporters MaeN (YufR) and YflS, and is essential for utilization of malate in minimal medium.
Microbiology (Reading): 2003, 149(Pt 9);2317-2329
[PubMed:12949159]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hans-Matti Blencke, Georg Homuth, Holger Ludwig, Ulrike Mäder, Michael Hecker, Jörg Stülke
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng: 2003, 5(2);133-49
[PubMed:12850135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Kei Asai, Sang-Hoon Baik, Yasuhiro Kasahara, Shigeki Moriya, Naotake Ogasawara
Regulation of the transport system for C4-dicarboxylic acids in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2000, 146 ( Pt 2);263-271
[PubMed:10708364]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ralf Rabus, Donald L Jack, David J Kelly, Milton H Saier
TRAP transporters: an ancient family of extracytoplasmic solute-receptor-dependent secondary active transporters.
Microbiology (Reading): 1999, 145 ( Pt 12);3431-3445
[PubMed:10627041]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)