Difference between revisions of "RemA"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 137: | Line 137: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | + | '''Additional publications:''' {{PubMed|22329926}} | |
<pubmed>,19363116, 19363116 23123912 </pubmed> | <pubmed>,19363116, 19363116 23123912 </pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 17:27, 4 January 2013
- Description: involved in the activation of biofilm matrix biosynthetic operons, acts in parallel to SinR, AbrB, and DegU
| Gene name | remA |
| Synonyms | ylzA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | regulator of the extracellular matrix |
| Function | control of biofilm formation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: remA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Nucleotides (regulation) | |
| MW, pI | 9 kDa, 7.178 |
| Gene length, protein length | 267 bp, 89 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yloC, gmk |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 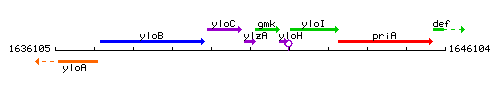
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15670
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: UPF0296 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: Q7WY72
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Daniel Kearns, Indiana University, Bloomington, USA, homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed