CymR
- Description: pleiotropic regulator of sulfur metabolism
| Gene name | cymR |
| Synonyms | yrzC |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcription repressor |
| Function | regulation of sulfur metabolism |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: cymR | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: CymR | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Riboflavin / FAD, Cys, Met & Sulfate assimilation | |
| MW, pI | 11 kDa, 9.879 |
| Gene length, protein length | 333 bp, 111 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yrvO, yrvN |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 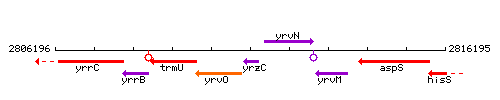
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
sulfur metabolism, transcription factors and their control, regulators of core metabolism
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The CymR regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU27520
Phenotypes of a mutant
- impaired growth in the presence of cystine and increased sensitivity to hydrogen peroxide-, disulfide-, paraquat- and tellurite-induced stresses PubMed
- increased intracellular cysteine pool and hydrogen sulfide formation PubMed
- depletion of branched-chain amino acids PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: Rrf2 family of transcription regulators
- Paralogous protein(s):
Genes repressed by CymR
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- UniProt: O34527
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Isabelle Martin-Verstraete, Institute Pasteur, Paris, France
Your additional remarks
References
The CymR regulon
Other original publications
Additional publications: PubMed
Marie-Françoise Hullo, Isabelle Martin-Verstraete, Olga Soutourina
Complex phenotypes of a mutant inactivated for CymR, the global regulator of cysteine metabolism in Bacillus subtilis.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 2010, 309(2);201-7
[PubMed:20608979]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Catherine Tanous, Olga Soutourina, Bertrand Raynal, Marie-Françoise Hullo, Peggy Mervelet, Anne-Marie Gilles, Philippe Noirot, Antoine Danchin, Patrick England, Isabelle Martin-Verstraete
The CymR regulator in complex with the enzyme CysK controls cysteine metabolism in Bacillus subtilis.
J Biol Chem: 2008, 283(51);35551-60
[PubMed:18974048]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Marie-Françoise Hullo, Sandrine Auger, Olga Soutourina, Octavian Barzu, Mireille Yvon, Antoine Danchin, Isabelle Martin-Verstraete
Conversion of methionine to cysteine in Bacillus subtilis and its regulation.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(1);187-97
[PubMed:17056751]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Soon-Yong Choi, Dindo Reyes, Montira Leelakriangsak, Peter Zuber
The global regulator Spx functions in the control of organosulfur metabolism in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(16);5741-51
[PubMed:16885442]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Pierre Burguière, Juliette Fert, Isabelle Guillouard, Sandrine Auger, Antoine Danchin, Isabelle Martin-Verstraete
Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis ytmI operon, involved in sulfur metabolism.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(17);6019-30
[PubMed:16109943]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Irina M Solovieva, Rimma A Kreneva, Lubov Errais Lopes, Daniel A Perumov
The riboflavin kinase encoding gene ribR of Bacillus subtilis is a part of a 10 kb operon, which is negatively regulated by the yrzC gene product.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 2005, 243(1);51-8
[PubMed:15668000]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christine Eymann, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Michael Hecker
Bacillus subtilis functional genomics: global characterization of the stringent response by proteome and transcriptome analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(9);2500-20
[PubMed:11948165]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)