Difference between revisions of "HprK"
(→Biological materials) |
|||
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | * '''Mutant:''' GP202 (spc), GP858 (aphA3), GP82 (cat), available in [[Stülke]] lab | + | * '''Mutant:''' GP202 (spc) {{PubMed|12055300}}, GP858 (aphA3) {{PubMed|18757537}}, GP82 (cat), available in [[Stülke]] lab |
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
Revision as of 17:04, 16 January 2014
| Gene name | hprK |
| Synonyms | ptsK, yvoB |
| Essential | no |
| Product | HPr kinase/ phosphorylase |
| Function | carbon catabolite repression, phosphorylation of HPr and Crh proteins at Ser46 |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: hprK | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: HprK | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: hprK | |
| MW, pI | 34 kDa, 4.906 |
| Gene length, protein length | 930 bp, 310 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | lgt, nagA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 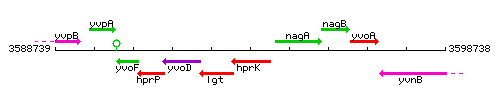
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
protein modification, transcription factors and their control
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU35000
Phenotypes of a mutant
no carbon catabolite repression
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + HPr = ADP + P-Ser-HPr (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: HPrK/P family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure: 1KKM (complex of Lactobacillus casei HprK with B. subtilis HPr-Ser-P), 1KKL (complex of Lactobacillus casei HprK with B. subtilis HPr)
- UniProt: O34483
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- for expression/ purification from B. subtilis with N-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, in pGP380: pGP642, available in Stülke lab
- for expression/ purification of mutant HprK-G158A from B. subtilis with N-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, in pGP380: pGP650, available in Stülke lab
- for expression/ purification from E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844: pGP205, available in Stülke lab
- for expression, purification of the N-terminal in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844: pGP218, available in Stülke lab
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody: available in Stülke lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Josef Deutscher, Paris-Grignon, France
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Wolfgang Hillen, Erlangen University, Germany Homepage
Anne Galinier, University of Marseille, France
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
General Analysis, Physiology
Isabelle Gaugué, Jacques Oberto, Harald Putzer, Jacqueline Plumbridge
The use of amino sugars by Bacillus subtilis: presence of a unique operon for the catabolism of glucosamine.
PLoS One: 2013, 8(5);e63025
[PubMed:23667565]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Frederik M Meyer, Matthieu Jules, Felix M P Mehne, Dominique Le Coq, Jens J Landmann, Boris Görke, Stéphane Aymerich, Jörg Stülke
Malate-mediated carbon catabolite repression in Bacillus subtilis involves the HPrK/CcpA pathway.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(24);6939-49
[PubMed:22001508]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kalpana D Singh, Matthias H Schmalisch, Jörg Stülke, Boris Görke
Carbon catabolite repression in Bacillus subtilis: quantitative analysis of repression exerted by different carbon sources.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(21);7275-84
[PubMed:18757537]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Holger Ludwig, Nicole Rebhan, Hans-Matti Blencke, Matthias Merzbacher, Jörg Stülke
Control of the glycolytic gapA operon by the catabolite control protein A in Bacillus subtilis: a novel mechanism of CcpA-mediated regulation.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 45(2);543-53
[PubMed:12123463]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J Reizer, C Hoischen, F Titgemeyer, C Rivolta, R Rabus, J Stülke, D Karamata, M H Saier, W Hillen
A novel protein kinase that controls carbon catabolite repression in bacteria.
Mol Microbiol: 1998, 27(6);1157-69
[PubMed:9570401]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Galinier, M Kravanja, R Engelmann, W Hengstenberg, M C Kilhoffer, J Deutscher, J Haiech
New protein kinase and protein phosphatase families mediate signal transduction in bacterial catabolite repression.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1998, 95(4);1823-8
[PubMed:9465101]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Structural Analysis of HPrK
Vincent Chaptal, Fanny Vincent, Virginie Gueguen-Chaignon, Vicente Monedero, Sandrine Poncet, Josef Deutscher, Sylvie Nessler, Solange Morera
Structural analysis of the bacterial HPr kinase/phosphorylase V267F mutant gives insights into the allosteric regulation mechanism of this bifunctional enzyme.
J Biol Chem: 2007, 282(48);34952-7
[PubMed:17878158]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Gregory S Allen, Katrin Steinhauer, Wolfgang Hillen, Jörg Stülke, Richard G Brennan
Crystal structure of HPr kinase/phosphatase from Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
J Mol Biol: 2003, 326(4);1203-17
[PubMed:12589763]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Sonia Fieulaine, Solange Morera, Sandrine Poncet, Ivan Mijakovic, Anne Galinier, Joël Janin, Josef Deutscher, Sylvie Nessler
X-ray structure of a bifunctional protein kinase in complex with its protein substrate HPr.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2002, 99(21);13437-41
[PubMed:12359875]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jose Antonio Márquez, Sonja Hasenbein, Brigitte Koch, Sonia Fieulaine, Sylvie Nessler, Robert B Russell, Wolfgang Hengstenberg, Klaus Scheffzek
Structure of the full-length HPr kinase/phosphatase from Staphylococcus xylosus at 1.95 A resolution: Mimicking the product/substrate of the phospho transfer reactions.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2002, 99(6);3458-63
[PubMed:11904409]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Enzymatic Properties, Mutation Analysis
HprK as a Target For Antimicrobial Compounds
Helena Ramström, Maryline Bourotte, Claude Philippe, Martine Schmitt, Jacques Haiech, Jean-Jacques Bourguignon
Heterocyclic bis-cations as starting hits for design of inhibitors of the bifunctional enzyme histidine-containing protein kinase/phosphatase from Bacillus subtilis.
J Med Chem: 2004, 47(9);2264-75
[PubMed:15084125]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)